A group of neuroscientists argue that our words are primarily for communicating, not for reasoning.
For thousands of years, philosophers have argued about the purpose of language. Plato believed it was essential for thinking. Thought “is a silent inner conversation of the soul with itself,” he wrote.
Many modern scholars have advanced similar views. Starting in the 1960s, Noam Chomsky, a linguist at M.I.T., argued that we use language for reasoning and other forms of thought. “If there is a severe deficit of language, there will be severe deficit of thought,” he wrote.
As an undergraduate, Evelina Fedorenko took Dr. Chomsky’s class and heard him describe his theory. “I really liked the idea,” she recalled. But she was puzzled by the lack of evidence. “A lot of things he was saying were just stated as if they were facts — the truth,” she said.
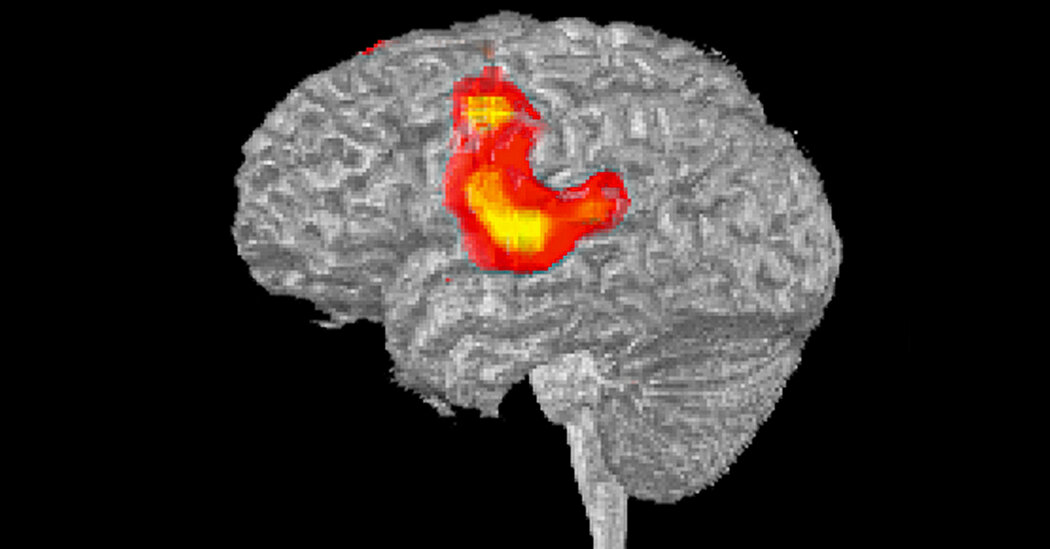
Dr. Fedorenko went on to become a cognitive neuroscientist at M.I.T., using brain scanning to investigate how the brain produces language. And after 15 years, her research has led her to a startling conclusion: We don’t need language to think.
“When you start evaluating it, you just don’t find support for this role of language in thinking,” she said.
When Dr. Fedorenko began this work in 2009, studies had found that the same brain regions required for language were also active when people reasoned or carried out arithmetic.